General Anesthesia & Sedation
Used For
Dental treatments under general anesthesia and sedation in dentistry are applied to pediatric and adult patients who are afraid or cannot be treated due to their systemic condition.
Timescale: 1 DAY
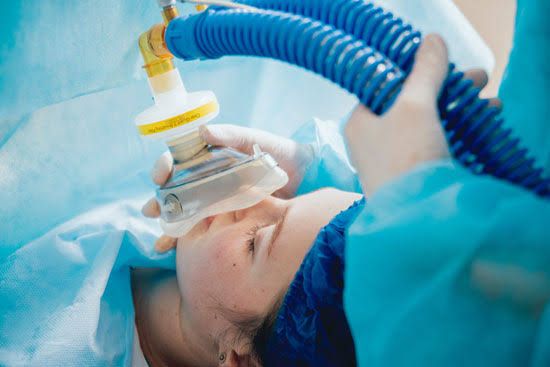
• Dental treatments under general anesthesia and sedation in dentistry are applied to pediatric and adult patients who are afraid or cannot be treated due to their systemic condition.
• Sedation is an anesthesia method performed by general anesthesia specialists and technicians in order to prevent pain, anxiety, fear and nausea that may occur during dental treatments.
• The patient who is asleep in the sedation method does not remember the pain and disturbing sounds of surgical procedures performed under the influence of sedative drugs. Sedation facilitates the patient's dental treatment in subsequent sessions. Sedation, which eliminates dental phobia, also destroys the perception of pain.
• Sedation should not be confused with general anesthesia. It does not carry the risks of general anesthesia as it is applied by sniffing sedative gas. After the application, the patient's recovery is fast.
General Anesthesia
• General anesthesia is the process of putting the patient to sleep with the drugs given under the control of the anesthesiologist before the operation or surgical procedure. When general anesthesia is given, the patient does not remember anything about the surgical procedure.
• The difference between sedation and general anesthesia is that in sedation the patient is semi-conscious.
• Dentists apply general anesthesia in situations that require fear, anxiety and advanced surgery.
What are the cases where dental treatments are performed under sedation or general anesthesia?
• In individuals with physical disabilities
• In individuals with mental (mental) disabilities
• Needing restorative or surgical treatment; However, in children and adults who cannot use local anesthesia due to acute infection, anatomical variations or allergies,
• In children or adults who cannot cooperate (communicate) despite the need for urgent treatment,
• In young children with common caries called bottle caries or early childhood caries,
• In cases where medical risks will decrease (such as some systemic disorders) if general anesthesia is applied,
• For children who need treatment in a single session for any reason (staying far away, risk of allergic reaction, etc.).